- Dialectical Behavioral Therapy Dbt Techniques
- Step By Step 13dialectical Behavioral Training Techniques
Jonathan Tarbox, Doreen Granpeesheh, in Evidence-Based Treatment for Children with Autism, 2014. Behavioral Skills Training. Behavioral Skills Training (BST) is a treatment package consisting of multiple treatment components that has been proven to be effective for training a wide variety of skills, simple and complex, in people in a wide variety of populations, including children and adults. About Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is an evidenced-based therapy designed to treat people who experience suicidal thinking and behaviors that are disruptive such as maladaptive coping skills and self harm. Step 1: Lay Down The Law. Step 2: Making The Medical Decisions. Step 3: New values—or adding the S to ‘he’ Step 4: Selecting The Image. Step 5: Proper Schooling. Step 6: Domestic Harmony Through Discipline. Step 7: The Coming Out Party. Step 8: His First Date- Calming The Jitters. Step 9: Positive Reinforcement For Princess. Behavioral health functional assessment includes the development of strategies to support the individual based upon assessment. Completed on 1:1 basis between the individual and either a behavioral support professional with a Master's Degree or under the direction of someone with a Master's Degree.
- Animal Training : Successful Animal Management Through Positive Reinforcement byISBN: 9780961107499Ken Ramirez wrote and edited this book as a training manual for his staff and for students of his graduate course on Animal Training. Published by the Shedd Aquarium in 1999 and now in its third printing, it has become the 'must have' book for zoo and aquarium trainers world-wide. The book is a collection of articles by over 100 trainers focusing on training topics ranging from beginner to advanced.
- Carrots and Sticks byISBN: 9780521686914Drawing on interviews with leading animal trainers, Carrots and Sticks offers 50 case studies that explore the step-by-step training of a wide variety of companion, working and exotic animals; reviews the preparation of animals prior to training and common pitfalls encountered. The book brings behavioural science to life, explaining animal training techniques in the language of learning theory.
- Kicked, Bitten, and Scratched byISBN: 9780670037681Graduates of the Exotic Animal Training and Management Program at California's Moorpark College land jobs in prestigious zoos, animal sanctuaries and research facilities, and they can be found in high-profile positions in Hollywood studios, the U.S. Navy and the organization Guide Dogs for the Blind. Sutherland chronicles the intriguing year she spent with students at this 'Harvard for exotic animal trainers,' accompanying the 'first years' as they interact with the exotic and not-so-exotic animals in the teaching zoo.
- Reaching the Animal Mind byISBN: 9780743297769A celebrated pioneer in the field of no-punishment animal training, Karen Pryor is responsible for developing clicker training--an all-positive, safe, effective way to modify and shape animal behavior--and she has changed the lives of millions of animals. Practical, engrossing, and full of fascinating stories about Pryor's interactions with animals of all sorts, 'Reaching the Animal Mind 'presents the sum total of her life's work. She explains the science behind clicker training, how and why it works, and offers step-by-step instructions on how you can clicker-train any animal in your life.
- Zookeeping : An Introduction to the Science and Technology byISBN: 9780226925318Zookeeping is a progressive textbook that seeks to promote consistency and the highest standards within global zoo and aquarium operations. Topics include: zookeeping; evolution of zoos; workplace safety; animal management; taxon-specific animal husbandry; animal behavior, enrichment and training; veterinary care; public education and outreach; and conservation science.
- AAZK Enrichment Notebook [CD-ROM] byISBN: 9781929672110
- Behavioral Enrichment in the Zoo byISBN: 0442251254
- Enriching Animal Lives byISBN: 9780983357919
- Zoo Animal Welfare byISBN: 9783642359545Zoo Animal Welfare thoroughly reviews the scientific literature on the welfare of zoo and aquarium animals. Maple and Perdue draw from the senior author's 24 years of experience as a zoo executive and international leader in the field of zoo biology. The authors' academic training in the interdisciplinary field of psychobiology provides a unique perspective for evaluating the ethics, practices, and standards of modern zoos and aquariums. The book offers a blueprint for the implementation of welfare measures and an objective rationale for their widespread use. Recognizing the great potential of zoos, the authors have written an inspirational book to guide the strategic vision of superior, welfare-oriented institutions. The authors speak directly to caretakers working on the front lines of zoo management, and to the decision-makers responsible for elevating the priority of animal welfare in their respective zoo. In great detail, Maple and Perdue demonstrate how zoos and aquariums can be designed to achieve optimal standards of welfare and wellness. --Provided by publisher.
- Zoo Animals : Behaviour, Management and Welfare byISBN: 9780199693528Zoo Animals: Behaviour, Management and Welfare addresses the key questions surrounding the keeping of exotic animals in captivity, and reveals how we can apply our ever-growing understanding of animal behaviour to ensure zoo animals are managed as effectively as possible. Drawing on their extensive experience of zoo research, practice, and teaching, the authors blend together theory with a broad range of both mammalian and non-mammalian examples to give a highly-readable overview of this burgeoning field. --Publisher.
During the last 20 years, a variety of terms have been coined to describe those life skills that allow individuals to self-care and function independently in society. Amongst these terms, you will find independent living skills, daily living skills, functional curriculum, functional skills, life skills and survival skills.
Although they may not describe the exact same set of skills, they all describe sets of skills that empower us to become independent adults successfully functioning in our communities.
Kids learn many of those skills through observation and imitation. But the reality for children with disabilities (cognitive, developmental, physical, sensory) may be different.
Life skills training is vital for them. Skills that most kids learn through observation may need to be specifically trained in kids with disabilities.
Table of Contents:
- Life Skills: Activities of daily living (ADLs) definition
- Why are ADLs so important
- Life Skills Training, Autism and/or Learning Disabilities
-Importance of life skills training for kids with disabilities
-Factors that may be affecting the acquisition of independent living skills - How can I teach my kid with autism and/or a learning disability independent living skills?
-Chaining Methods
-Prompting Strategies
-Additional Tips - Independent Living Skills Checklist
Life Skills: Activities of daily living definition.
Activities of daily living (ADLs) are those things we normally do in daily living including any daily activity we perform for self-care such as feeding ourselves, bathing, dressing, grooming, work, homemaking, and leisure. The ability or inability to perform ADLs can be used as a very practical measure of ability/disability in many disorders.
Source: MedicineNet
The concept of ADLs was coined by Sidney Katz, the American scientist and educator who developed the Index of Independence of Activities for Daily Living.
ADLs can may be split in two categories: Basic ADLs and Instrumental ADLs.
Basic ADLs
Basic ADLs are the self-care skills that are fundamental for your everyday life functioning.
These activities would include:
- Dressing
- Feeding
- Bathing/Showering
- Personal Hygiene
- Toileting
Instrumental ADLs (IADLs)
IADLS are skills that are not necessary for fundamental functioning but empower you to function independently in the community.
Examples of activities that would fall in this category would be the ones related to:
- Home maintenance
- Transportation/Mobility
- Money management
- Personal safety and health care
- Community participation
- Communication and interpersonal relationships
- Leisure and recreation
Why are Activities of Daily Living Important?
Activities of daily living:
- Allow us to take care of ourselves
- Empower us to participate independently in society
- May be a factor in medical decision making
- May serve as a guidance as to the level of support/ assistance an individual needs
- Lack of performance may highlight areas that need training/instruction
Life Skills Training, Autism and/or Learning Disabilities
Importance of life skills training for kids with disabilities
Why is it important to trained kids with autism or learning disabilities in independent living skills?
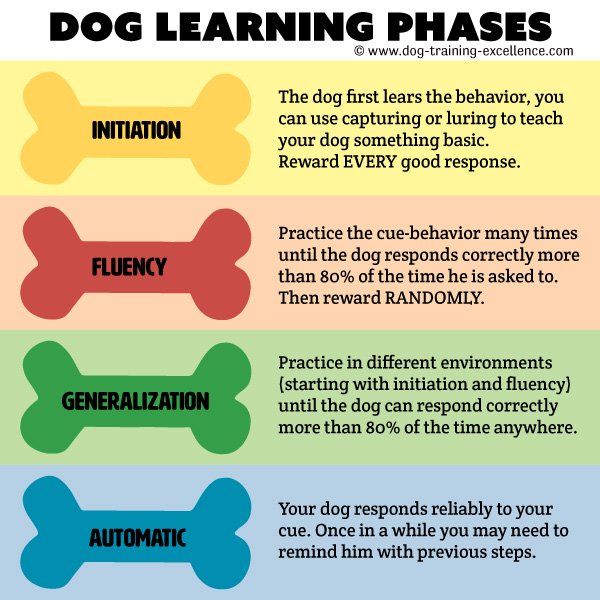
Skills that most kids learn through observation may need to be specifically trained in kids with disabilities.
Even autistic teens with good cognitive abilities present in approximately 50% of cases a daily living skills deficit.
Research on life skills training and intervention for students with learning disabilities suggests that:
- Life skills are appropriate for all students
- Life skills should be part of the school curriculum
- Vocational training is an important skill to cover
- Life skills are best taught in the natural context
- Life skills should be addressed daily
- Parental understanding of life skills instruction can be advantageous
- Challenges to teaching life skills do exist
- Transition planning is important to overall quality of life
Source: Life Skills Curricula for Students with Learning Disabilities: A Review of the Literature – Mary E. Cronin
Factors that may be affecting the acquisition of independent living skills in kids with autism and/or learning disabilities
What may be interfering with the development of those independent living skills?
Some of the reasons behind this reality may be:
- A deficit in attention skills
- Interfering behaviors
- Sensory issues
- Lack of motivation, not understanding the social motivations for self-care
- An absence of prerequisite skills
- Motor skills issues
Some other times, us parents are unintentionally depriving them of learning opportunities by:
- Being overprotective
- Underestimating their skills
- Going the easy route and doing everything for them
How can I teach my kid with learning disabilities or autism new independent living skills?
Kids with learning disabilities or autism may need to be specifically trained to learn new skills. Chaining is an instructional method very appropriate to teaching life skills.
What is a Chaining Method?
A new skill can be looked at as a chain of individual tasks or steps in a sequence Each step of the sequence will be reinforced and trained individually. There are several types of chaining methods depending on what step of the routine you start training.
Types of Chaining Methods
Forward Chaining.
Every step in the chain is taught in the naturally occurring order. Success on the first step is reinforced (for example, praised), and training proceeds to the next step only when the first step has been successfully trained.
Total-Task Chaining.
This is a variation of the previous method. In this method, the complete chain is taught in every session
Backward Chaining.
The training starts with the last step of the sequence. It only moves to the next step once the last step has been successfully trained.
If you wish to read more on Chaining Methods (step-by-step examples) please, check my post: Teaching Life Skills in Special Education: Chaining
Prompting Strategies
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy Dbt Techniques
In order to train each step of the chain we may need to use different promoting strategies (listed from most invasive to less invasive):
- Physical prompts – physically guiding your kid through the response
- Modeling – we model the step/ behavior that we want to teach
- Gesture prompts – gesturing or pointing to the correct response
- Verbal prompts –
- Visual prompt –pictures or texts that support learning the sequence.

Additional Tips When Using Prompts to Support Instruction
When using prompts to support instruction it is important to:
- Use the least invasive level of prompting required, and
- Remove the prompt as soon as possible in order to allow the independent accomplishment of the steps.
Independent Living Skills Checklist
If you are looking for inspiration on what life skills you could be considering teaching to your child, you are welcome to download our own checklist that includes 100+ life skills.
This is not a checklist by age. I find those checklists a bit overwhelming as they remind me of all the milestones that we have missed. Instead, it is a general list of skills that are important and that we need to keep in mind when we choose what skills to target.
For us, parents of kids with special needs, our choices will be influenced by factors like:
- Skills already acquired
- Skills they will have more opportunities to practice and maintain
- Areas where they have more learning difficulties
- “Easy wins”
- Skills that will have more impact on their independence
Download your Independent Life Skills Checklist below:
Step By Step 13dialectical Behavioral Training Techniques
Other resources for parents with kids with autism or special needs
- Autism Elopement Prevention: 30 Tips to Prevent Autism Wandering
- Autism & Head Banging: How to Prevent it or Minimize Harm
- Music Therapy & Autism: How to Improve 18 Valuable Skills
- Autism & Anxiety: Triggers & Calming Strategies